Because of pillows behind the head and shoulders the hypothetical patient is at 35.
Blood pressure beach chair position.
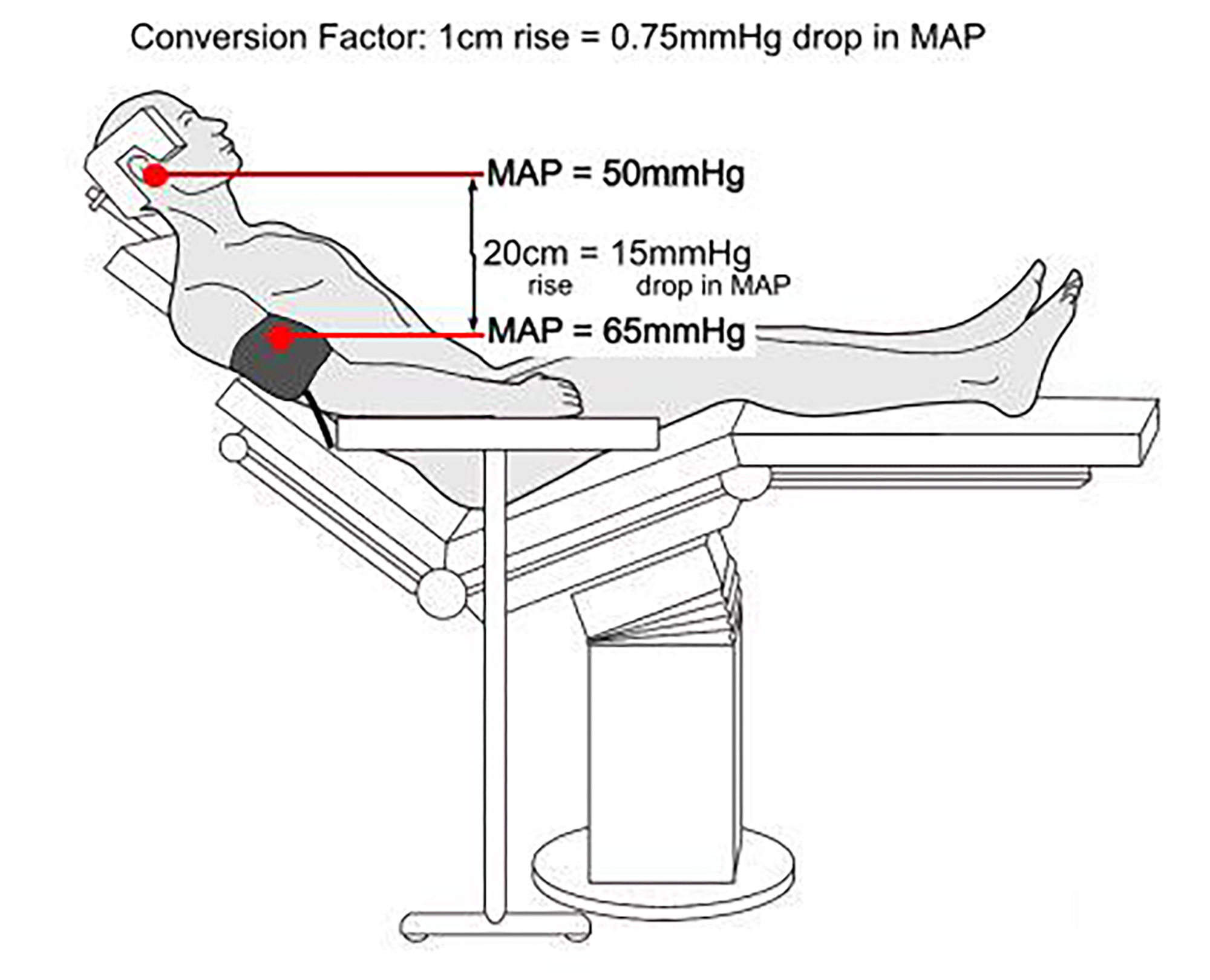
Hence while doing shoulder surgery in an upright position if a blood pressure reading for a cuff placed at the level of the heart is 120 80 mmhg and there is 25 cm of elevation between it and the external auditory meatus the cerebral pressure is 102 62.
The beach chair position is often used for nasal surgeries abdominoplasty and breast reduction surgeries.
Allow for hydrostatic gradient and keep the blood pressure up no widely agreed monitoring standard increasing fio 2 and etco 2 results in a measurable improvement in cerebral oxygenation for patients anesthetized in the beach chair position anesthetic agents have differing effects on the brain but there is no.
The sitting and beach chair position bcp are variations of nearly the same position with similar physiologic changes and potential complications.
The blood pressure drop 5 min after beach chair position measured at the acoustic meatus level in the cde group was higher compared to patients without cdes p 0 009 as was the rsco2 p 0 039.
The vertical distance from the circle of willis ac represents the pressure gradient between those sites and the blood pressure.
This can result in brain damage but an understanding of cerebral autoregulation is essential to prevent this occurrence.
When positioning a patient in fowler s position the surgical staff should minimize the degree of the patient s head elevation as much as possible and always.
Cerebral blood flow is at risk when cerebral blood pressure falls.
Blood pressure management during beach.
An even more exaggerated occurrence may develop when the bp cuff must be placed on the leg because the contralateral arm is not available for bp measurement e g in a patient with prior lymph node dissection for.
Figure 58 1 modified beach chair position established on a standard operating room table set at 30 above the horizontal plane.
In patients who are anesthetized for surgery in the beach chair position brain blood pressure can fall to levels below the brain s ability to autoregulate.
Further studies are needed to define the incidence of adverse neurological adverse events in the beach chair position identify the best intraoperative neurological monitors that are predictive of neurocognitive outcomes the lowest safe acceptable blood pressure during surgery for individual patients and the optimal interventions to treat.
If the beach chair position is combined with the use of deliberate hypotension cerebral perfusion will be severely compromised.