Based on the 5 year survival rate stage 4 bile duct cancer prognosis intrahepatic bile duct cancer prognosis and distal and perihilar bile duct cancer prognosis is only 2.
Bile duct adenocarcinoma prognosis.
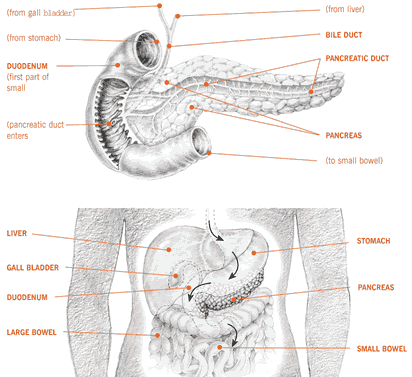
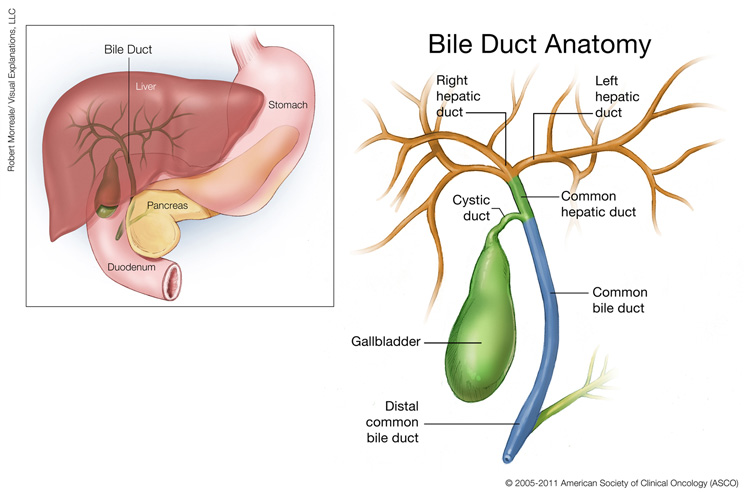
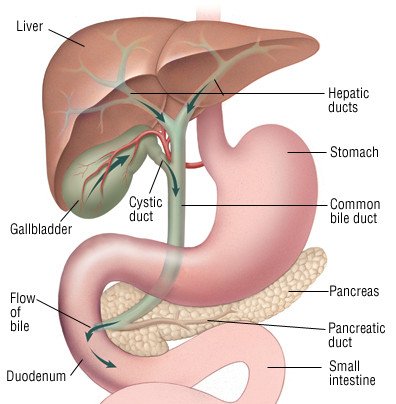
Bile duct cancer is a rare disease in which malignant cancer cells form in the bile ducts.
Prognosis is worse for those patients whose tumor has invaded adjacent tissues has lymph node involvement or has spread to distant places in the body.
For more advanced bile duct cancers nearby liver tissue pancreas tissue or lymph nodes may be removed as well.
It is produced by the liver and accumulated in the gallbladder.
If untreated bile duct cancer survival is 50 at one year 20 at two years and 10 at three years with virtually no survival at five years.
If the cancer has spread to a distant part of the body the 5 year survival rate is 2.
Bile duct problems present at birth.
Complete surgical removal of the tumor remains the only chance for cure however 80 90 of patients have disease that is surgically incurable at the time of clinical presentation 15.
When possible doctors try to remove as much of the cancer as they can.
Bile goes from the gallbladder directly into the small intestine in order to help in the process of digestion.
For example if the 5 year relative survival rate for a specific stage of bile duct cancer cholangiocarcinoma is 30 it means that people who have that cancer are on average about 30 as likely as people who don t have that cancer to live for at least 5 years after being diagnosed.
Having colitis or certain liver diseases can increase the risk of bile duct cancer.
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma pdac is the most common malignancy of the pancreas.
If the cancer is diagnosed at an early stage the 5 year survival rate is 24.
Bile duct cancer begins in the defective bile duct itself.
Bile is the digestive fluid which helps in breaking down fats.
If the cancer has spread to the regional lymph nodes the 5 year survival rate is 7.
Pdac is an aggressive and difficult malignancy to treat.
The tnm staging system provides a detailed summary of how far the bile duct cancer has spread and gives doctors an idea about a person s prognosis outlook.
In areas of southeast asia cholangiocarcinoma is associated with liver fluke infection which can occur from eating raw or undercooked fish.
People born with a choledochal cyst which causes dilated and irregular bile ducts have an increased risk of cholangiocarcinoma.
Tests that examine the bile ducts and nearby organs are used to diagnose and stage bile duct cancer.
The 5 year survival rate for intrahepatic bile duct cancer is 8.
For very small bile duct cancers this involves removing part of the bile duct and joining the cut ends.
The common bile duct cancer prognosis for stage 1 increases to 15 and for stages 2 and 3 by 6 for intrahepatic bile duct cancer.